Last year, as life sciences organizations were consumed by the recovery from COVID-19, their focus had to shift rapidly to mitigating supply chain constraints, labor and skill shortages, and by the end of the year, inflationary pressures—all of which were exacerbated by the Russia-Ukraine war.
Along with these challenges, the ongoing drive to reduce costs, improve efficiency and productivity, drive better decision-making and reduce risk will continue to drive pharma investment in cloud, AI/ML, analytics and automation in 2023 despite higher interest rates.
Organizations must rethink their business models to serve a variety of strategic goals, and AI will play an increasingly important role in all of them: supporting drug discovery, trial diversity, forecasting and supply chain functions, and supporting engagement and adherence to decentralized trials and on-market regimens. These shifts will set the stage for further industry transformation as gene therapy and precision health become more widely available.
The macro-environment favors steady long-term focus and growth
The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 puts pressure on companies to reduce drug and device prices in the USA, causing pharma to leverage technology to drive cost efficiencies and maintain margins. Globally, the shifting policy debate around access and affordability of patented pharmaceuticals exerts additional pressures. An inflationary environment will slow down traditional R&D and leave pharma no choice but to investigate AI/ML and related techniques to accelerate drug discovery and repurposing while reducing costs. This will also stimulate new partnerships (for example, pharma companies working with research labs or providers working with payers) through federated learning and cloud-based digital ecosystems.
Manufacturing costs and costs of clinical trials will continue to rise. The cost of active pharmaceutical ingredients has increased by up to 70% since 2018. Recruiting on-site patients and maintaining on-site trials remains prohibitively expensive. Pharma will focus on digital patient recruitment through social advertising and digital engagement (including wearables) throughout trials to manage adherence and persistence. Decentralized trial structures will push pharma to focus more closely on cybersecurity and protected health information (PHI) while managing the associated costs.
The costs of operating manufacturing facilities will increase as energy prices continue to rise. We predict companies will make significant strides towards digitization to reduce cost, improve quality, reduce recalls and improve safety. Pre-digital facilities with manual processes supported by expensive labor will no longer be the norm.
Strategy 1: Prioritize around novel drug development, generics or consumer engagement
Strategic reprioritization should be top of mind for the C-suite. Last year, Pfizer and GSK left the consumer health sector to prioritize novel drug and vaccine development and core innovation. We saw targeted mergers and acquisitions to replenish pipelines, which will continue in 2023. Novartis spun off Sandoz, their generics business, and is streamlining their research efforts around innovative pharmaceuticals. Sanofi and the generics giant Sun Pharmaceuticals are repositioning to enter specialty pharma with the latter releasing a new highly competitive biologic for psoriasis.
Companies are recognizing that divergent business models are required: innovative pharma requires significant capital investments to support state-of-the-art research enabled by new technology, while generic and consumer health business models demand unparalleled scale, access to distribution and close partnerships with pharmacies. A rising risk-return ratio for innovators will lead companies to form research and technology partnerships that combine top talent with the most innovative computation techniques, rather than outright mergers or acquisitions.
Strategy 2: Use AI-driven forecasting and supply chains to improve operational efficiency and sustainability
The upheaval and disruption caused by COVID-19 has given pharma leaders a heightened awareness of resiliency in delivering innovative drugs and therapeutics to communities, underscoring the importance of investing in forecasting and supply chains.
Forecasting
Forecasting continues to be a pain point for many organizations. According to a recent IBM IBV study, 57% of CEOs view the CFO as playing the most crucial role in their organizations over the next two to three years. Legacy processes, demand volatility and increasing data scale and complexity demand a new approach. Traditional quarterly forecasting cycles (which are manual and burdensome) yield inaccurate predictions.
Leading companies will invest in AI, ML and intelligent workflows to deliver end-to-end forecasting capabilities that utilize real-time feeds from multiple data sources, leveraging hundreds of AI and ML models, to deliver more granular and accurate forecasts and customer insights. These capabilities will fundamentally change the role of finance organizations by emphasizing speed of insight, adoption of data-driven decision making and scaling of analytics within the enterprise.
Supply chain
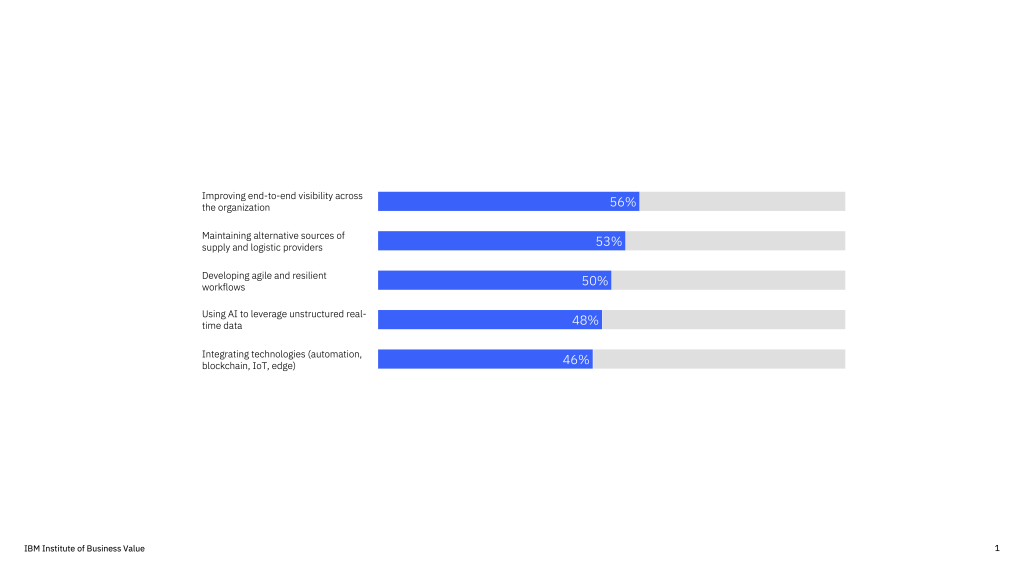
Business leaders will focus on supply chain solutions that drive transparency across sourcing, manufacturing, delivery and logistics while minimizing cost, waste and time. CSCOs are modernizing supply chain operations by using AI to leverage unstructured data in real time and integrating automation, blockchain and edge computing to manage operations and collect and connect information across multiple sources.
In the wake of COVID-19, we observe leaders viewing the supply chain as a core organizational function rather than a supportive one. David Volk, executive director of clinical supply chain planning at Roche states, “We are a networked organization… collaborating much more broadly across all our partners and the industry. We view ourselves as a supply chain organization, and a significant part of the value we bring to patients lies in optimizing our global supply chain and inventory. That’s a very different mindset, and it’s changed how we run the organization.”
Supply chain sustainability also ranks among the highest priorities for CEOs. 48% of CEOs surveyed say increasing sustainability is a top priority—up 37% since 2021. 44% cite a lack of data-driven insights as barriers to achieving sustainability objectives. End-to-end visibility into sustainability impact, such as metrics on emissions and waste from raw material to delivery, will unlock a new level of information that position CSCOs as key enablers for companies to achieve their sustainability and ESG vision.
Strategy 3: Prepare for an influx of cell and gene therapies
Gene therapy is the new frontier of medicine. It focuses on targeting a person’s genes for modification to treat or cure disease, including cancer, genetic diseases and infectious diseases. The US Food & Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first gene therapy in the United States in 2017. Since then, more than 20 cell and gene therapy products have been approved.
According to the Alliance for Regenerative Medicine, we could see five more gene therapies for rare diseases introduced to the U.S. market in 2023, including new treatments for sickle cell disease, Duchenne muscular dystrophy and hemophilia.
These therapies will challenge life sciences organizations to rethink their business models. How will they efficiently determine which patients are eligible for these therapies? How will they obtain the patient’s blood as part of the therapy? How will they contract with payers for reimbursement, given these therapies can cost upwards of $3M per treatment? How will they track outcomes from treatment for outcome-based agreements? These questions and many more spanning payment models, consumer experience, supply chain and manufacturing will need to be addressed.
A key driver in the growth of gene therapies and adoption of precision health is the growth and accessibility of next-generation DNA sequencing (NGS). NGS will become more mainstream, moving the science out of the lab to deliver improved patient care and outcomes at scale. NGS delivers ultra-high throughput, scalability and speed and has revolutionized the industry by enabling a wide variety of analyses across multiple applications at a level never before possible. This includes delivering whole-genome sequencing at accessible and practical price points for researchers, scientists, doctors and patients. An example is the new Illumina NovaSeq X sequencer released in September 2022, which is twice as fast as prior models and capable of sequencing 20,000 genomes per year at a cost of $200 per genome. As the price of sequencing genomes declines, the ability to support personalized healthcare and gene therapy at scale will continue to grow.
Strategy 4: Accelerate development and delivery of lifesaving therapies through decentralized clinical trials
Limitations of traditional clinical trials were amplified during the COVID-19 pandemic and have accelerated the use of decentralized clinical trials (DCTs). There is a clear need to improve study formats so broader, more equitable populations are accessed and included. New technologies will help integrate patient data points and derive holistic insights like never before. Life sciences organizations will increase their use of DCTs to run global studies and bring new therapies to market. We expect a record number of decentralized trials in 2023.
Key benefits of DCTs include:
- Faster recruitment. Participants can be identified and engaged without the need to travel and be evaluated in person.
- Improved retention. Participants are less likely to drop out of a trial due to the typical in-person requirements.
- Greater control, convenience and comfort. Participants are more comfortable engaging at home and at local patient care sites.
- Increased diversity. Participants in legacy trials lacked diversity and contributed to gaps in understanding of diseases.
As DCTs are more broadly adopted, designing trials around the patient experience will be critical to ensuring clear, transparent engagement and willing and active participation. Methodologies such as Enterprise Design Thinking® can provide a useful framework. Likewise, integrating patient data from multiple sources such as electronic health and medical records, electronic data capture platforms, clinical data management systems, wearables and other digital technologies will require a more open approach to information sharing.
Quantum computing will enable more advanced DCT capabilities for recruitment, trial site selection, and optimization and patient surveillance. Quantum-based algorithms can outperform existing computer algorithms, enabling better analysis of integrated patient data at scale.
In the coming years, decentralized trials will become the norm, improving the ability to recruit, select and deliver clinical trials at scale, ensuring full and diverse populations are represented and lifesaving treatments are more quickly approved and launched.
Strategy 5: Explore AI-driven drug discovery
AI-driven drug discovery continues to gain momentum and achieve critical milestones. The first AI-designed drug candidate to enter clinical trials was reported by Exscientia in early 2020. Since then, companies such as Insilico Medicine, Evotec and Schrödinger have announced phase I trials. Several candidates have had their clinical development accelerated through AI-enabled solutions. Within drug companies focused on AI-based discovery, there is publicly available information on about 160 discovery programs, of which 15 products are reportedly in clinical development.
Some execs may think AI can be delivered through the “tool in the public cloud” or by a single team. From our experience working with life sciences companies, this is not the case. Achieving full value from AI requires transformation of the discovery process spanning new tech, new talent and new behaviors throughout the R&D organization.
The AI-driven discovery process delivers value across four dimensions: finding the right biological target, designing a small molecule as a preclinical candidate, improving success rates and delivering overall speed and efficiency.
Search for new biological targets
We see the research community and industry scientists pursuing integration of multiomics and clinical data with machine learning to achieve drug repositioning. Leveraging experimental data and literature analysis, it is possible to uncover new disease pathways and polypharmacological and protein interactions. Application of AI to imaging (and other diagnostic techniques that rigorously analyze phenotypic outputs) may offer opportunities to identify new biological targets. Some of our clients look to understand protein interactions, function and motion using traditional computation techniques as well as quantum computing.
Use new techniques to search for new molecules
Using a deep search technique, it is possible today to mine the research literature and published experimental data to predict new small molecule structures and how molecules will behave. This and other techniques can be used to predict pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties and help identify off-target effects.
Explore the promise of quantum computing
Since 2020, there have been numerous quantum-related activities and experiments in the field of life sciences, spanning genomics, clinical research and discovery, diagnostics, treatments and interventions. Quantum-driven machine learning, trained on diverse clinical and real-world data sets, has been applied to molecular entity generation, diagnostics, forecasting effectiveness and tailoring radiotherapy.
Strategy 6: Use digital engagement to increase sales efficiency, patient loyalty and adherence
For healthcare providers
Conventional face-to-face visits to healthcare providers (HCPs) have reached the limit of effectiveness. HCPs now expect personalized approaches and instant access to knowledge. Increased scrutiny by public authorities, along with COVID-19, disrupted a traditional approach where sales reps had HCP offices and hospitals as their second home. A virtual engagement model emerged that is less effective in its current form.
At the same time, industry sees the value of an omnichannel HCP engagement strategy: our analysis shows 5-10% higher satisfaction with a new HCP experience, 15-25% more effective marketing spend, 5-7% boost in active prescribers and up to 15% lift in recurring revenue depending on the indication.
Pharma companies have enough data on certain products to enable a personalized experience for HCPs. An analytics and AI-driven approach to engagement with clinicians provides the highest impact as it improves both their speed-to-decision and their awareness of the latest clinical evidence. Well-defined technology and data strategies, along with change management and talent identification programs, are key to success.
For patients
Adherence and persistence are major challenges in an industry that caters to chronic patients. Additionally, with new reimbursement models, payers incentivize “complete” cases that achieve prolonged remission or, for acute patients, functional recovery. To keep selling meds and getting paid for them, patients need to be taking them continuously. For many indications, patients have many pharmaceutical options. Successful companies will differentiate themselves in the market by offering digital support for their pharmaceuticals, engaging patients in their care on their smartphones through gamification and incentive programs.
Bills and regulations will increase the adoption and application of AI
AI underpins the trends mentioned above. While AI technology has been around for decades, its adoption in life sciences has accelerated over the last several years, impacting drug development, clinical trials and supply chains. AI is infused into many of our daily interactions, from calling an airline to rebook tickets, asking Alexa to play music and turn on the lights, receiving an approval for a loan, to providing automated treatment recommendations to patients based on their clinical history and the latest treatment guidelines.
As AI continues to permeate our lives, oversight will be front and center. Both the United States and EU consider regulation to be essential to the development of AI tools that consumers can trust. Life sciences companies must understand the impact AI regulations have on their business models and that they play a proactive role in influencing these policies in the interest of better patient outcomes.
As an example, IBM’s Policy Lab takes a proactive approach to providing policymakers with a vision and actionable recommendations to harness the benefits of innovation while ensuring trust in a world being reshaped by data. IBM works with organizations and policymakers to share our perspective to support responsible innovations. One such bill was the Biden-Harris administration’s Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights released in September 2022. As stated in the Bill, “AI systems have the potential to bring incredible societal benefits, but only if we do the hard work of ensuring AI products and services are safe and secure, accurate, transparent, free of harmful bias and otherwise trustworthy.” The Bill lays outs five commonsense protections to which everyone in America should be entitled in the design, development and deployment of AI and other automated technologies:
- Right to safe and effective systems. You should be protected from unsafe or ineffective systems.
- Algorithmic discrimination protections. You should not face discrimination by algorithms, and systems should be used and designed in an equitable way.
- Data privacy. You should be protected from abusive data practices via built-in protections and have agency over how your data is used.
- Notice and explanation. You should know that an automated system is being used and understand how and why it contributes to outcomes that impact you.
- Human alternatives, consideration and fallback. You should be able to opt out where appropriate and have access to a person who can quickly consider and remedy problems you encounter.
The application of AI is not slowing down, nor is scrutiny of it. Life sciences organizations will differentiate themselves by having a seat at the table. They will seek opportunity to influence AI-health policy and deliver ethical and responsible AI-powered solutions that augment their existing product portfolio and improve patient and provider experiences and healthcare outcomes at reduced costs.
Embrace new technologies to offer major advances
Life sciences companies, particularly in pharma and biotech, can prove resilient despite inflationary pressures. They must focus on business model specialization across innovation and invention, generics business and consumer health. Strong demand can help companies overcome business challenges and position the industry for steady innovation-led growth. It is crucial to embrace new technologies, particularly state-of-the-art computing and AI, to offer major advances that may represent a paradigm shift in drug discovery, clinical trial site optimization, and, ultimately, engagement with a person receiving care. Acting boldly in 2023 with a clearly articulated strategy and prioritization will set both mature life sciences organizations and new players on the right path. Companies that focus on strategy and innovation will be the biggest winners.
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- Platoblockchain. Web3 Metaverse Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- Source: https://www.ibm.com/blogs/internet-of-things/life-sciences-innovation-six-strategies-2023/