Table of contents
An operating system (OS) manages all other applications and programs in a computer, and it is loaded into the computer by a boot program. It enables applications to interact with a computer’s hardware. Through a designated application programme interface, the application programmes request services from the operating system (API). The kernel is the software that contains the operating system’s core components. To run other programmes, every computer has to have at least one operating system installed.
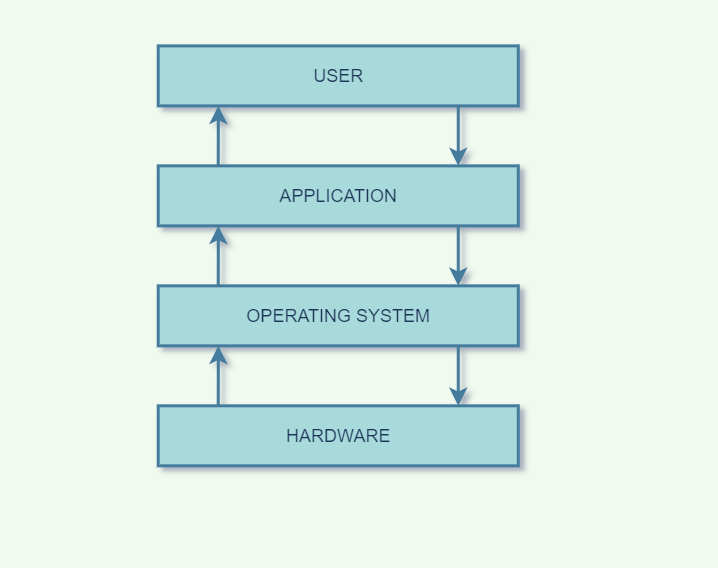
Windows, Linux, and Android are examples of operating systems that enable the user to use programs like MS Office, Notepad, and games on the computer or mobile phone. It is necessary to have at least one operating system installed in the computer to run basic programs like browsers.
Functions of Operating System
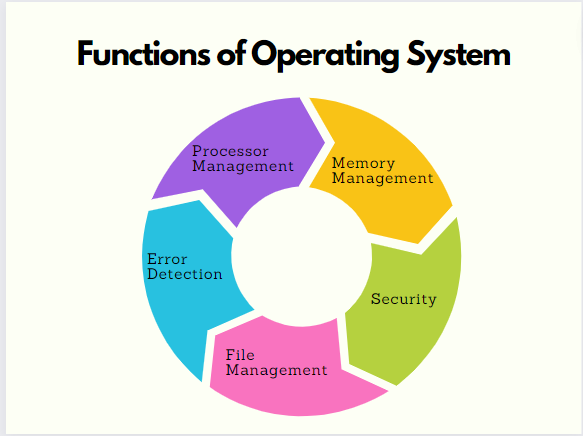
The functions of an operating system (OS) are diverse and crucial for the efficient operation of a computer system. These functions include:
- Memory Management: The OS manages the main memory, allocating and deallocating it as necessary for various processes. It ensures that different processes can coexist in memory without interfering with each other.
- Processor Management/Scheduling: This involves managing the CPU’s time and resources among the various processes. The OS selects which processes receive CPU time and ensures efficient and fair use of the processor.
- Device Management: The OS regulates the connection and interaction with various input and output devices through device drivers. It allocates and deallocates devices to different processes and keeps track of device statuses.
- File Management: The OS manages files on a computer, handling tasks like creation, deletion, transfer, and storage. It also maintains the integrity and security of the data within these files.
- Storage Management: The OS is responsible for storing and accessing files and directories, optimizing the use of various storage devices, and ensuring data integrity and efficient retrieval.
- Security: Modern OSs employ security measures like firewalls to protect against unauthorized access and intrusion. They monitor system activity and block potential threats.
- Job Accounting and System Performance Control: The OS keeps track of all system activities, including memory, resource usage, and errors. It also monitors performance indicators to ensure efficient operation.
- Error Detection: The OS continually checks for system errors and threats, protecting the system from potential damage and alerting users to take appropriate action.
- Coordination Between Software and Users: It coordinates hardware components and directs various software applications, ensuring smooth operation and user interaction.
In addition to the traditional functions of an operating system (OS), there are several advanced and evolving functions that modern OSs are increasingly incorporating:
- Virtualization Support: Modern OSs often include support for virtualization, allowing multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical machine. This facilitates efficient resource utilization and isolation of different computing environments.
- Cloud Integration: Many operating systems now offer built-in cloud integration, enabling seamless access to cloud storage and services, and facilitating data synchronization and backup across devices.
- Energy Management: With the growing use of mobile devices, OSs are increasingly focused on energy management to extend battery life. This includes optimizing the use of hardware resources and managing background processes.
- Advanced Security Features: Modern OSs are equipped with advanced security features such as biometric authentication, encryption, advanced firewall and anti-malware systems, and continuous security updates to protect against emerging threats.
- Automated Updates and Maintenance: OSs now often include automated system updates and maintenance features, ensuring that the system stays up to date with the latest features and security patches without requiring manual intervention.
- IoT Support: With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, operating systems are being designed to support IoT applications, including managing and interacting with a vast array of sensors and smart devices.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Incorporating AI and machine learning algorithms for predictive analytics, personalization, and enhanced user interaction is becoming a key feature in modern operating systems.
These additional functionalities reflect the evolving nature of operating systems as they adapt to new technological advancements and user needs.
Features of Operating Systems
Here is a list of some important features of operating systems:
- Provides a platform for running applications
- Handles memory management and CPU scheduling
- Provides file system abstraction
- Provides networking support
- Provides security features
- Provides user interface
- Provides utilities and system services
- Supports application development
Advantages of Operating System
There are several advantages of operating systems. We have listed some of them below:
- Ensuring correct and efficient use of the computer’s hardware.
- Allowing different applications to run concurrently.
- Managing files and folders.
- Providing a user interface.
- Managing security.
- Managing resources.
- Managing printing.
- Providing a platform for software development.
Disadvantages of Operating System
There are several disadvantages of operating systems. We have listed some of them below:
- They can be complex and difficult to use.
- They can be expensive to purchase and maintain.
- They can be vulnerable to attacks from malicious users.
Types of Operating Systems
The types of operating systems (OS) have evolved significantly, adapting to technological advancements and changing user needs. Here’s a summary of various types of operating systems:
- Batch OS: Traditionally used for executing a series of jobs without manual intervention. While still relevant in specific contexts, modern computing has largely moved beyond batch processing due to the rise of more interactive and real-time systems.
- Distributed OS: These systems manage a network of interconnected computers, distributing the workload among them. They are becoming increasingly relevant with the rise of cloud computing and edge computing. Distributed systems are critical for handling large-scale, distributed applications efficiently.
- Multitasking OS: These systems, capable of running multiple tasks simultaneously, continue to evolve. Modern multitasking OSs are more efficient at resource allocation, ensuring smoother operation even with numerous applications running.
- Network OS: These are designed to manage networked computers, providing shared access to resources like files and printers. With the proliferation of cloud services, network operating systems are increasingly integrating cloud functionalities for enhanced connectivity and resource sharing.
- Real-Time OS (RTOS): RTOSs are crucial in scenarios where time-critical operations are necessary, such as in embedded systems, robotics, and IoT devices. They ensure timely processing and responses, a key requirement in autonomous systems and industrial automation.
- Mobile OS: Mobile operating systems have seen significant advancements, particularly in terms of integration with cloud services, security features, and user interface enhancements. The focus has shifted towards seamless synchronization across devices and platforms, providing a consistent user experience.
- IoT Integration: Modern operating systems are evolving to better manage and integrate with a growing number of IoT devices. They are becoming central in controlling and monitoring these devices, offering unified interfaces for diverse smart devices.
- AR/VR Support: There’s an increased focus on supporting augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies. Future operating systems are expected to offer optimized environments for AR/VR applications, with advanced capabilities in graphics rendering, motion tracking, and spatial audio.
- Enhanced Security and Privacy: With digital threats becoming more sophisticated, operating systems are emphasizing stronger security measures and privacy controls. This includes advanced encryption techniques, secure boot processes, and user-centric privacy features.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: The trend is towards operating systems that provide seamless integration and compatibility across various devices and platforms. This includes cloud storage integration and universal app frameworks for a consistent multi-device experience.
- Edge Computing and Distributed Systems: As computing extends beyond traditional data centers, operating systems are adapting to manage resources in distributed architectures, including edge computing scenarios. This trend is geared towards faster and more responsive applications.
- Machine Learning and Predictive Capabilities: Operating systems are increasingly leveraging machine learning for predictive analytics and optimization. This includes intelligent power management and personalized user experiences.
Single-tasking vs. multi-tasking operating systems: Single-tasking operating systems allow only one program to run at a time, while multi-tasking operating systems allow multiple programs to run simultaneously. Desktop vs. mobile operating systems: Desktop operating systems, such as Windows and macOS, are designed for use on desktop and laptop computers, while mobile operating systems, such as iOS and Android, are designed for use on smartphones and tablets. Open-source vs. proprietary operating systems: Open-source operating systems are developed by a community of developers and are available for free, while proprietary operating systems are developed by a single company and must be purchased.
Components of Operating System
- Shell
- Kernel
What is Shell?
Shell handles user interactions. It is the outermost layer of the OS and manages the interaction between user and operating system by:
- Prompting the user to give input
- Interpreting the input for the operating system
- Handling the output from the operating system.
Shell provides a way to communicate with the OS by either taking input from the user or the shell script. A shell script is a sequence of system commands that are stored in a file.
For an in-depth understanding of this topic, check out this free operating system course.
What is Kernel?
The kernel is the core component of an operating system for a computer (OS). All other components of the OS rely on the core to supply them with essential services. It serves as the primary interface between the OS and the hardware and aids in the control of devices, networking, file systems, and process and memory management.
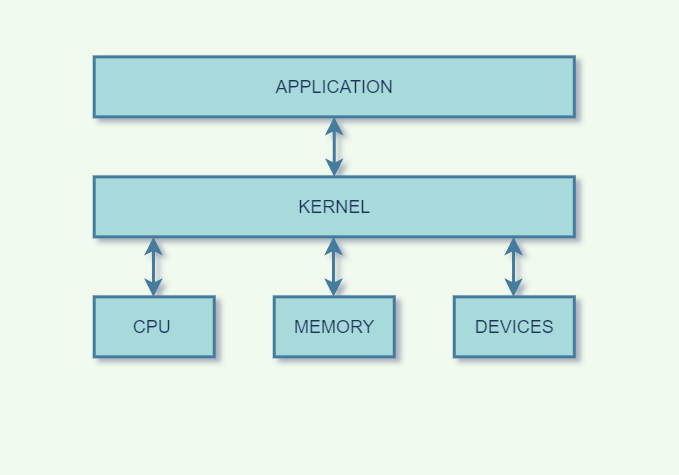
Functions of kernel
The kernel is the core component of an operating system which acts as an interface between applications, and the data is processed at the hardware level.
When an OS is loaded into memory, the kernel is loaded first and remains in memory until the OS is shut down. After that, the kernel provides and manages the computer resources and allows other programs to run and use these resources. The kernel also sets up the memory address space for applications, loads the files with application code into memory, and sets up the execution stack for programs.
The kernel is responsible for performing the following tasks:
- Input-Output management
- Memory Management
- Process Management for application execution.
- Device Management
- System calls control
Earlier, all the basic system services like process and memory management, interrupt handling, etc., were packaged into a single module in the kernel space. This type of kernel was called the Monolithic Kernel. The problem with this approach was that the whole kernel had to be recompiled for even a small change.
In a modern-day approach to monolithic architecture, a microkernel contains different modules like device management, file management, etc. It is dynamically loaded and unloaded. With this modern-day approach, the kernel code size was reduced while its stability increased.
Types of Kernel
Linus Torvalds introduced the concept of a monolithic kernel in 1991 as a part of the Linux kernel. A monolithic kernel is a single large program that contains all operating system components. However, the Linux kernel evolved over the years and now consists of different types of kernels, as listed below.
1. Monolithic Kernel As the name suggests, a monolithic kernel is a single large program that contains all operating system components. The entire kernel executes in the processor’s privileged mode and provides full access to the system’s hardware. Monolithic kernels are faster than microkernels because they don’t have the overhead of message passing. This type of kernel is generally used in embedded systems and real-time operating systems.
2. Microkernel A microkernel is a kernel that contains only the essential components required for the basic functioning of the operating system. All other components are removed from the kernel and implemented as user-space processes. The microkernel approach provides better modularity, flexibility, and extensibility. It is also more stable and secure than monolithic kernels.
3. Hybrid Kernel A hybrid kernel is a kernel that combines the best features of both monolithic kernels and microkernels. It contains a small microkernel that provides the essential components for the basic functioning of the OS. The remaining components are implemented as user-space processes or as loadable kernel modules. This approach provides the best of both worlds, namely, the performance of monolithic kernels and the modularity of microkernels.
4. Exokernel An exokernel is a kernel that provides the bare minimum components required for the basic functioning of the operating system. All other components are removed from the kernel and implemented as user-space processes. The exokernel approach provides the best possible performance because there is no kernel overhead. However, it is also the most difficult to implement and is not widely used.
Now let’s look at the different types of operating systems.
32-bit OS versus 64-bit OS
| Parameter | 32-Bit OS | 64-Bit OS |
| Data and Storage | The 32 bit OS can store and manage less data than the 64 bit OS, as its name would imply. It addresses a maximum of 4,294,967,296 bytes (4 GB) of RAM in more detail. | In contrast, the 64 bit OS has a larger data handling capacity than the 32 bit OS. It indicates that a total of 264 memory addresses, or 18 quintillion gigabytes of RAM, can be addressed. |
| Compatibility of System | A 32-bit processor system will run only on 32-bit OS and not on 64 bit OS. | A 64-bit processor system can run either a 32-bit or 64-bit OS |
| Application Support | The 32-bit OS support applications with no hassle. | The 64-bit OS do not support applications. |
| Performance | Performance of 32- bit OS is less efficient. | Higher performance than the 32-bit processor. |
| Systems Available | These support Windows 7, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 8, and Linux. | These support Windows XP Professional, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows Vista, Linux, and Mac OS X. |
Popular Operating Systems
Some of the most popular operating systems in use today include:
- Windows: Windows is the most popular desktop operating system, used by over 1 billion users worldwide. It has a wide range of features and applications, including the Office suite, gaming, and productivity tools.
- macOS: macOS is the desktop operating system used by Apple Mac computers. It is known for its clean, user-friendly interface and is popular among creative professionals.
- Linux: Linux is an open-source operating system that is available for free and can be customized to meet specific needs. It is used by developers, businesses, and individuals who prefer an open-source, customizable operating system.
- iOS: iOS is the mobile operating system used by Apple iPhones and iPads. It is known for its user-friendly interface, tight integration with Apple’s hardware and software, and robust security features.
- Android: Android is the most popular mobile operating system, used by over 2 billion users worldwide. It is known for its open-source nature, customization options, and compatibility with a wide range of devices.
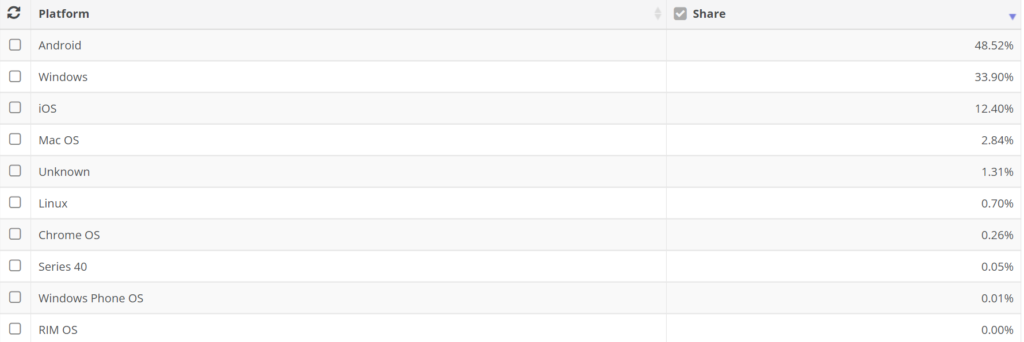
Operating Systems Market Share

Choosing the Right Operating System
When choosing an operating system, there are several factors to consider, including:
- Cost: Some operating systems, such as Linux, are free, while others, such as Windows and macOS, must be purchased.
- Compatibility: Some software and hardware may only work with certain operating systems, so choosing an operating system compatible with your needs is important.
- Ease of use: Some operating systems, such as macOS and iOS, are known for their user-friendly interfaces, while others, such as Linux, may have a steeper learning curve.
- Security: Some operating systems, such as macOS and iOS, are known for their robust security features, while others, such as Windows, may be more vulnerable to security threats.
Operating System Generations
Operating systems have evolved over time through different generations, each marked by distinct characteristics and advancements. Let’s explore these generations along with real-time examples:
1. First Generation:
- Time Period: 1940s to early 1950s
- Characteristics: Vacuum tubes and machine language programming.
- Example: ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) – One of the earliest computers that used vacuum tubes for calculations.
2. Second Generation:
- Time Period: Late 1950s to mid-1960s
- Characteristics: Transistors and assembly language programming.
- Example: IBM 1401 – Used transistors, enabling faster and more reliable processing than vacuum tubes.
3. Third Generation:
- Time Period: Mid-1960s to mid-1970s
- Characteristics: Integrated circuits (ICs) and high-level programming languages.
- Example: IBM System/360 – Introduced a family of computers using compatible software and peripheral devices.
4. Fourth Generation:
- Time Period: Late 1970s to 1990s
- Characteristics: Microprocessors, personal computers, and graphical user interfaces (GUI).
- Example: Apple Macintosh – Introduced GUI and mouse-driven interface, making computers more user-friendly.
5. Fifth Generation:
- Time Period: 1990s to present (continuing)
- Characteristics: Artificial Intelligence (AI), natural language processing, and parallel processing.
- Example: IBM’s Deep Blue – Defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997, showcasing the power of AI in complex decision-making.
6. Sixth Generation (Speculative):
- Characteristics: Advanced AI, quantum computing, brain-computer interfaces.
- Example: Quantum computers being developed by companies like IBM and Google, potentially revolutionizing complex calculations.
7. Future Generations (Hypothetical):
- Characteristics: Even more advanced AI, integration with human cognition, new computing paradigms.
- Example: A future generation could involve computers that seamlessly interface with the human brain, enabling direct thought-based interactions.
These generations demonstrate how operating systems have evolved from basic machine-level instructions to sophisticated systems that can handle complex tasks and interactions with users. Each generation builds upon the achievements of the previous one, incorporating new technologies and capabilities.
Conclusion
As the need for technology grows day by day in the coming days and as younger generations like Gen Alpha grow up & join the workforce good & efficient operating system will be the topmost priority of every business setting. If you are planning to get a degree in IT, now is the best time to start.
Operating System FAQs
An operating system (OS) is the programme that controls all other application programmes in a computer after being installed into the system first by a boot programme. The application programmes seek services from the operating system (API) through a specified application programme interface.
An operating system facilitates communication between a user and a system. Examples of operating systems are Microsoft Office, Notepad, and gaming on a computer or mobile device including Windows, Linux, and Android.
Types of an Operating System are
Batch Operating System.
Time-Sharing Operating System.
Distributed Operating System.
Embedded Operating System.
Real-time Operating System.
The most crucial piece of software that runs on a computer is the operating system. It controls the memory, operations, software, and hardware of the computer. Using this method, you can converse with the computer even if you don’t understand its language.
An operating system is a design that enables user application programmes to communicate with the hardware of the machine. The operating system should be built with the utmost care because it is such a complicated structure and should be simple to use and modify. Partially developing the operating system is a simple approach to accomplish this.
A process is an instance of a computer programme that is being run by one or more threads in computing. It includes the programme code and all of its operations. A process may consist of several concurrently running threads of execution, depending on the operating system (OS).
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- PlatoHealth. Biotech and Clinical Trials Intelligence. Access Here.
- Source: https://www.mygreatlearning.com/blog/what-is-operating-system/



