Digital Payment Adoption Heightens Fraud Risks
The COVID-19 pandemic has sped up the shift towards electronic payments, which is unlikely to reverse anytime soon, if ever. Credit cards were the most vulnerable payment method to online scams in 2022, with an estimated $1,034 billion in e-commerce sales.
However, fraud has become more common than ever, with 127 million Americans being victims of credit card fraud in 2021.
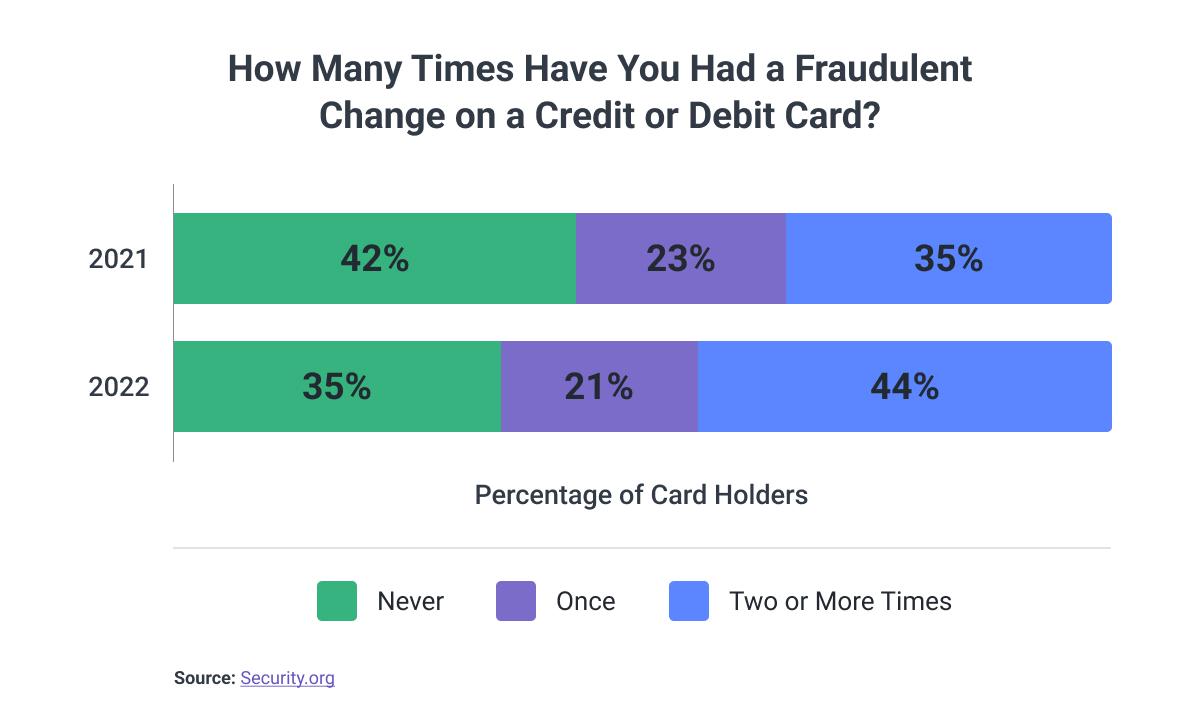
Approaches for Fraud Detection and Prevention
Banks, neobanks, and other financial institutions can leverage emerging technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence to detect and prevent fraud.
With these technologies, it has become possible to alert cardholders to act before fraudsters remove a significant amount of money from their credit or debit cards.

Approaches for Fraud Detection and Prevention
Credit card fraud is the criminal use of another person’s credentials or credit standing, and it falls into two categories: card-present and card-not-present fraud.
Criminals use physical cards or card details to make fraudulent purchases. In some cases, card-not-present crime is accompanied by account takeover techniques, where fraudsters contact a credit card issuer and pretend to be a legitimate cardholder to change information associated with the account.
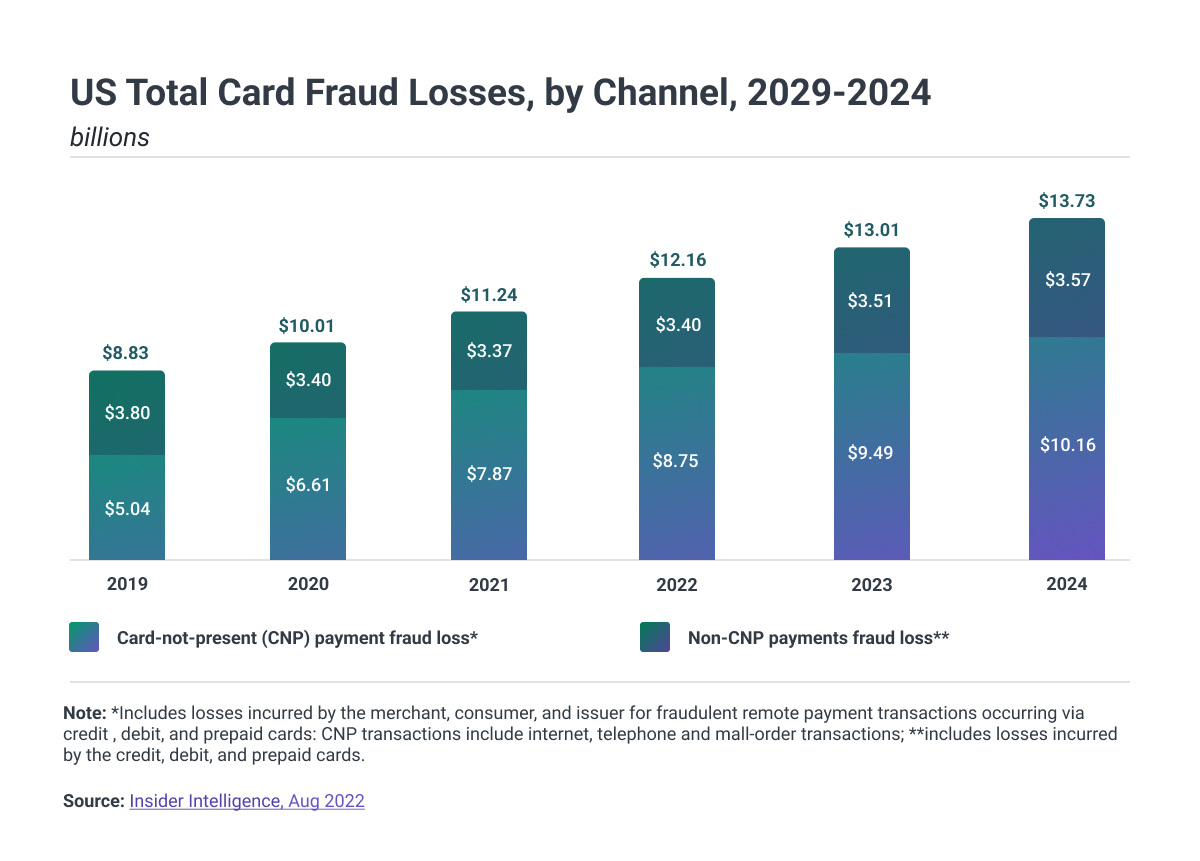
How Financial Institutions Detect Fraud
Banks, card issuers, and other financial institutions are utilizing different policies, tools, methodologies, and practices to combat identity fraud and stop fraudulent transactions.
These institutions are employing a variety of technologies, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, that use vast amounts of data to learn user patterns, flag problematic transactions, and react on time.
How Financial Institutions Prevent Fraud
Preventing credit card fraud is a significant goal for financial institutions.
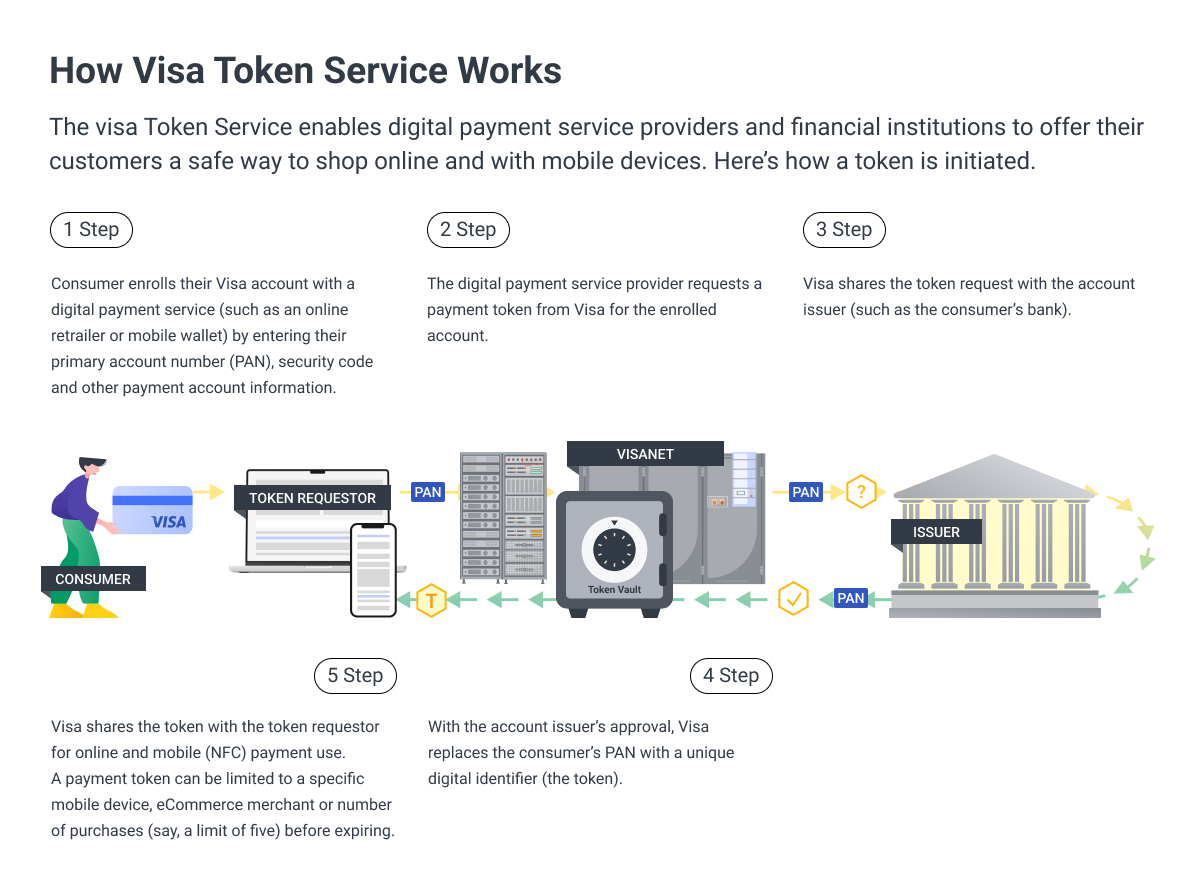
Tokenization is a process of replacing credit card numbers with randomly generated numbers impossible to trace back. This method ensures that payment transactions don’t contain any original information, reducing the risk of fraud. In addition, financial institutions use rules to help find patterns in fraudulent activity and alert the cardholder.
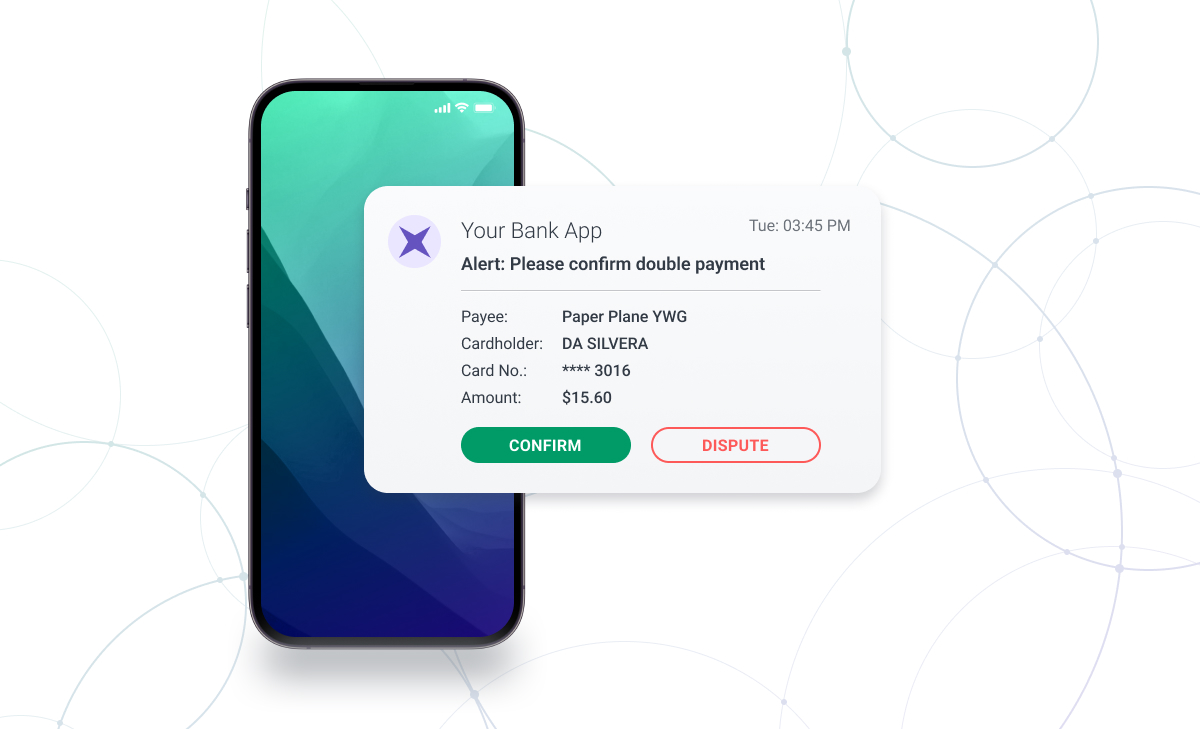
Confirming banking transactions is another way to prevent fraud. Banks send a confirmation request to a cardholder’s phone, which must be verified before the transaction is approved. This ensures that the cardholder authorized the transaction, preventing fraudulent activity.
Financial institutions and networks have categorized fraudulent behavior into 4 types:
- E-commerce and remote payments fraud
- Counterfeit fraud
- Lost and stolen cards
- Account takeovers and other types of fraud
Tools for Fraud Prevention and Detection
Technologies and strategies for combating fraud are designed to fight all four mentioned types of fraud. All major banks and credit card companies are working on heightening security measures and improving their internal processes for fraud detection.
Since banks and credit card companies have to absorb much of the financial liability of credit card fraud, they are heavily invested in preventing fraud by all means. Here are some of the most common approaches to fighting credit card fraud.
Consumer Transaction Alerts
Consumer transaction alerts are a powerful way to stop any fraudulent action before it damages the cardholder’s account. Notifications and alerts are usually sent to the cardholder’s mobile phone, email, or banking application. Every alert is an indication that a transaction has been initiated.
SMS Text Alerts
SMS Text Alerts not only help identify fraud attempts as they happen but also give retail customers a greater sense of control and confidence.
Call Center-Based Multi-Factor Authentication
In addition to offering 2-factor authentication on the web, there is now multi-factor authentication technology for call centers, including both full-service and remote facilities.
Agents issue a token to the mobile device on file for an account and ask the caller to authenticate the transaction in real-time. Authentication is currently invoked for certain fraud-sensitive transactions and events and can be expanded on as required in the future.
Dynamic Passcodes
A dynamic code is a one-time unique code required to verify the transaction sent to the cardholder via the banking app, emails, or as SMS. This ensures a high level of security as it authenticates a cardholder according to the regulatory requirements of the PSD2 Directive.
Real-time Data Enrichment Tools
Real-time data is useful for enhancing KYC data with aggregate extra data obtained from a variety of sources like open-source databases, digital services, and social networks. This tool is helpful in fraud detection as it provides additional information on each cardholder.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning has become one of the cornerstones of fraud detection. It’s a system that helps gather and interpret as much data possible about cardholders and use it to establish purchasing patterns.
When fraudsters use card information in a new location, alerts, typing speed information, and new phone recognition. Also, if the transaction was done in a strange time the system can flag those transactions and make sure the cardholder knows what’s going on.
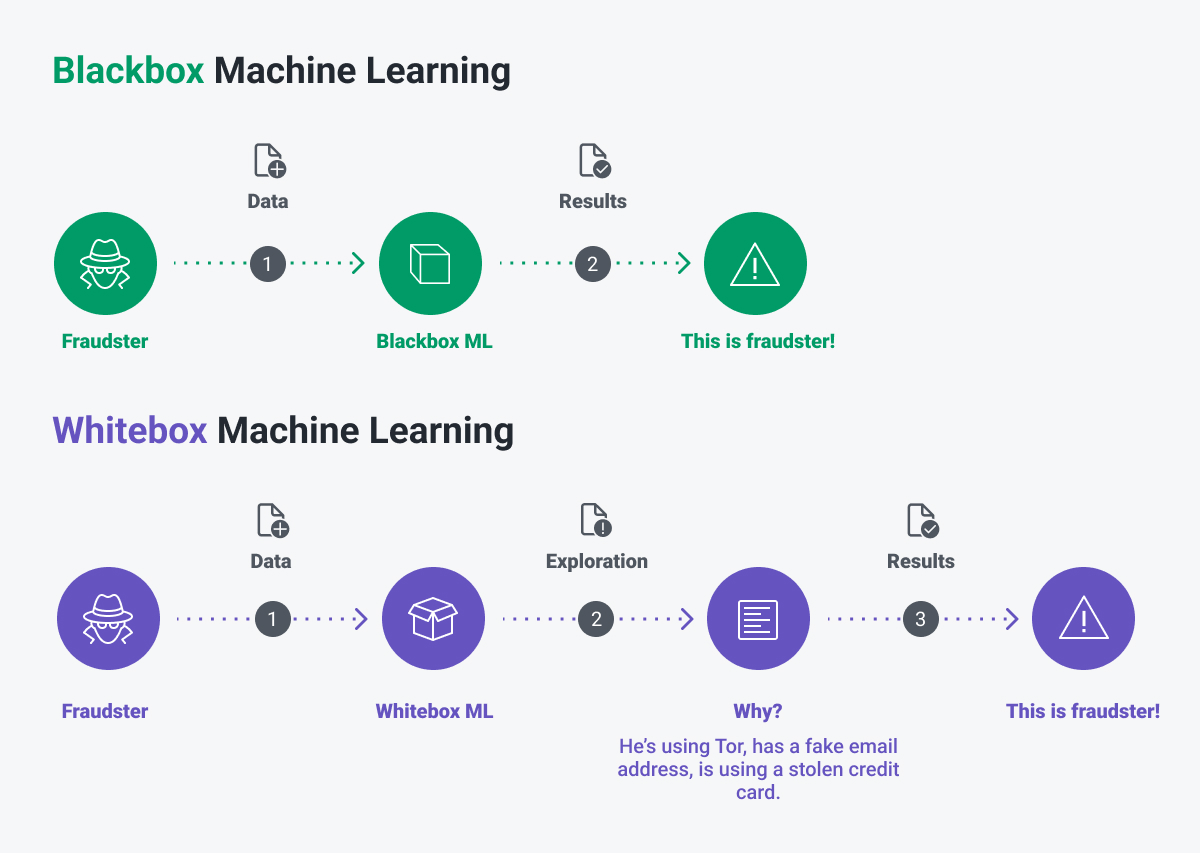
The black box fraud prevention system is a machine learning model that helps prevent card fraud. These systems are becoming more and more popular as they are fast to give a credit card risk score pinpointing what factors are likely to lead to risky transactions.
There are two types of machine learning, black box and white box. After 2021, most systems in use are black box, since this type of ML uses new technologies like big data, string similarities, deep learning, and neural networks.
Know Your Customer (KYC)
KYC is a significant approach to fighting financial fraud. It is designed to perform identity verification on a variety of levels (like ID verification), thus allowing financial institutions to meet compliance requirements and prevent fraud for their customers.
The KYC process includes ID, face, document, and biometric verification. For example, in India, banks can use e-KYC which allows them to verify people’s identities through a separate government-verified application.
Voice Biometrics
Voice biometrics is a new technology being used by financial institutions and banks to passively authenticate callers based on their voiceprint. By comparing a caller’s voice characteristics against a verified, previously enrolled voice sample, this technology can help identify fraudsters and flag calls made under duress. It also automates the authentication process for shareholders, allowing them to access their accounts faster.
Enhanced Knowledge-Based Authentication (KBA)
Enhanced Knowledge-Based Authentication
(KBA) is another technology being used to prevent credit card fraud. KBA validates cardholder identities against outside sources, such as a person’s social security number, date of birth, phone number, and address. By checking whether personal information provided by a caller appears in association with the same individual in other records, KBA can create extremely hard-to-guess challenge questions.
Adaptive Authentication
Adaptive authentication is an AI fraud risk scoring capability that will pull together analytics from multiple channels to provide clear guidance to agents during a call. By combining anomalies such as unusual device attributes, excessive numbers of transactions, or failed voiceprints into a single risk score, agents can take the appropriate actions to prevent fraud before it happens.
Address Verification Service or AVS
Address Verification Service (AVS) is one of the most widely used fraud prevention tools in card-not-present (CNP) transactions. AVS compares the billing address used in the transaction with the issuing bank’s address information for the cardholder to ensure that the purchase goes to the customer’s address.
Geolocation
Geolocation matches a cardholder’s mobile phone location with the location of a transaction, offering one more data point when accepting or declining a transaction. It may work in conjunction with other tools, such as sending the consumer a unique passcode on their mobile to confirm that they are initiating the transaction.

Account Takeover Tools
Account takeover tools detect account takeover attempts through biometric authentication, activity analytics that compare current online behavior with past established patterns, and general card verification. Card verification methods, such as card verification value (CVV) or card verification code (CVC), are required in CNP transactions where a PIN cannot be used.
Final Word
By digitizing fraud prevention capabilities using AI and other advanced technologies, banks and financial institutions can speed up their response to fraud and help cardholders feel more comfortable moving to digital payments.
As payment fraud continues to be a serious problem, taking steps to protect users and their accounts is essential. The use of anti-fraud tools and continually improving them and discovering new techniques and technologies year after year is vital to combat payment fraud.
Don’t let payment fraud hinder your business growth! Leverage a software partner who deeply understands the payments industry and can support companies that offer prepaid or credit cards with the anti-fraud solutions their cardholders will appreciate.
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- Platoblockchain. Web3 Metaverse Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- Minting the Future w Adryenn Ashley. Access Here.
- Source: https://www.finextra.com/blogposting/24049/the-latest-technologies-for-banks-to-detect-and-prevent-credit-card-fraud?utm_medium=rssfinextra&utm_source=finextrablogs



