Remote Work Insights | Jun 10, 2024

 Image: WEF Realizing the Potential of Global Digital Jobs (White paper cover)
Image: WEF Realizing the Potential of Global Digital Jobs (White paper cover)The Effects of Global Digital Jobs on Canadian Markets
The World Economic Forum (WEF) has published a white paper last month called ‘Realizing the Potential of Global Digital Jobs‘ covering the possibilities, difficulties, and solutions connected with global digital jobs, as remote work continues to reshape the global labour environment. This article looks at the effects on fintech businesses in Canada, unintended consequences for urban commercial districts and a range of remote working trends to stay on top of.
Global Digital Jobs
The WEF report anticipated that by 2030, there will be 92 million remote digital workers globally, up from 73 million that exist today. This indicates a considerable shift towards remote work. The number of people in economies with lesser incomes that have higher levels of education are growing. Educated individuals capable of filling global digital positions have surged in nations like India and Nigeria. By optimizing talent use and lowering skill mismatches across nations, global digital jobs could increase global GDP by $11 trillion by 2030.
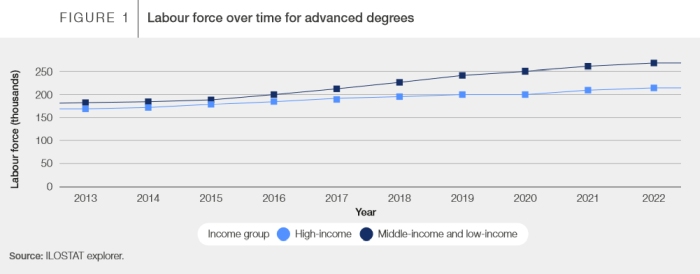
 Chart: WEF Realizing potential of Global Digital Jobs: Figure 1 – Advanced Degree Labour Force Over Time
Chart: WEF Realizing potential of Global Digital Jobs: Figure 1 – Advanced Degree Labour Force Over TimeThis is an interesting trend, given that there’s currently a skills shortage across a number of industries in Canada. Looking at Figure 1 chart above, one can see that the total labour force pool available with advanced degrees from lower to middle income countries has increased significantly over the years. This means that more and more highly skilled digital workers are coming from lower-income nations, who can help companies fill employment gaps prevalent in higher-income economies while creating jobs for people in need.
See: Debunking the Work/Life Balance Myth with Scott Galloway
For this global digital jobs framework to work, remote workers need strong tech infrastructure, digital tools, high speed internet and a country to operate out of with simplified work and tax requirements that make economic sense. For companies relying on remote workers to plug gaps, it is essential to spend money on education and training to develop and integrate the applicable hard and soft skills.
Access to Global Talent Pools
Global talent pools can boost innovation and give the fintech industry a competitive edge. Remember, many countries have amassed years of fintech experience compared to Canadian markets due to their progressive regulatory landscapes and openness to foster a globally competitive market. Fintech organizations can reduce operational expenses without sacrificing talent quality by employing remote workers from areas with cheaper cost of living.
However, there are risks. Managing the many labour and tax laws in several nations can be difficult and resource-intensive. To keep out of legal hot water, businesses must stay abreast of regulatory developments and make sure they are compliant. There is also a greater chance of cybersecurity breaches as remote employment increases. Strong cybersecurity procedures are a top priority for Canadian fintech companies in order to safeguard sensitive financial data.
See: Game-changer for Remote Work? Introducing the AR Laptop by Spacetop
It can also be difficult to integrate remote workers into an existing corporate culture. Businesses must put plans in place to foster healthy team relationships and a cohesive work environment. To avoid discontent and social isolation among remote workers, this involves advocating for equitable compensation and maintaining a work-life balance.
What About Skilled Canadian Digital Workers?
The growth in global digital jobs offers opportunities and challenges for competent digital workers in Canada. On one hand, there’s more competition from potentially less expensive global digital workers, on the other hand, it’s never been easier to experience working for a global company from the comfort of their own home, which can increase their job and income earning potential like never before.
To stay ahead of the curve, Canadian workers must embrace learning new skills continuously and invest in ongoing education, particularly in the areas of developing technologies and in-demand skills.
See: Visa’s Solutions for the Creator Economy and Fintech Opportunities for Tomorrow’s Digital SMBs
Canadian professionals can make a lasting impression by cultivating a strong online personal brand on platforms such as LinkedIn where they can share and demonstrate their knowledge, exchang ideas, and network with company prospects globally. Canadian workers must get up to speed with international employment trends, markets and figure out their core value propositions. It could be for example to help an international brand interested in entering Canadian markets.
Unexpected Consequences for Urban Markets
Commercial real estate in major Canadian cities like Toronto, Vancouver, and Montreal have been adversely impacted by the transition to remote employment. For instance, by the end of 2023, Toronto’s downtown office vacancy rate had reached a record high of 17.4%. There is less demand for traditional office premises as a result of this trend, which is indicative of a larger shift towards remote work and hybrid models.
Local businesses have also been impacted by this rise in vacancy rates. Local companies that depend on office workers’ foot traffic are impacted by the decline in the demand for office space. Downtown businesses such as restaurants, shops, and other services are seeing a drop in revenue. In addition, developers are finding it difficult to find tenants for brand-new office space, which is leading them to think about converting commercial buildings into residential or mixed-use ventures.
See: Double-Edge Sword of AI’s Impact on Workforce Experience
To create more dynamic and resilient urban centres, cities are thinking about approving a greater number of mixed-use complexes, which include residential, commercial, and recreational areas. In order to alleviate the housing shortage, several business buildings are being converted into residential units in Toronto and Montreal, where this trend is especially noticeable.

 Freepik jcomp, global digital workers
Freepik jcomp, global digital workersRemote Work Trends
- It is anticipated that the hybrid work model—which blends remote and in-office employment—will become the standard. This will have an impact on plans for urban development and the use of office space.
- Businesses will probably rearrange offices to encourage teamwork and community involvement, turning them into gathering places for sporadic in-person gatherings.
- As businesses look to reduce the risks brought on by international supply chains, geopolitical unrest, and complicated regulations, many are also choosing to ‘onshore’ business activities locally to maintain stronger operational, compliance, and data security management.
- And then there’s ‘nearshoring‘ which is outsourcing work to neighbouring nations’ talent pools like the US and Mexico that have comparable time zones and cultural affinities. Reducing time zone and cultural headaches associated with offshoring, can provide a balance between cost savings and operational effectiveness.
See: LinkedIn: Top In Demand Fintech Jobs In Canada
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing the nature of remote work by improving decision-making, automating repetitive tasks, and boosting productivity. However, it brings up concerns of workforce displacement and cost-effectiveness. AI systems demand a large initial infrastructure and technological investment. Once put into practice, though, they can readily scale and manage massive task volumes with incredible precision and consistency. Over time, AI will save operating costs since it can process data and complete repetitive jobs more quickly than people.
Closing Thought
Globalization of the digital workforce brings opportunities and risks for Canadian markets, particularly in the fintech industry. Canadian companies must work strategically by tapping into global talent while being proactive about cybersecurity and regulatory issues. The next few years will be super interesting in determining how firms and urban centres respond to these disruptive developments.

 The National Crowdfunding & Fintech Association (NCFA Canada) is a financial innovation ecosystem that provides education, market intelligence, industry stewardship, networking and funding opportunities and services to thousands of community members and works closely with industry, government, partners and affiliates to create a vibrant and innovative fintech and funding industry in Canada. Decentralized and distributed, NCFA is engaged with global stakeholders and helps incubate projects and investment in fintech, alternative finance, crowdfunding, peer-to-peer finance, payments, digital assets and tokens, artificial intelligence, blockchain, cryptocurrency, regtech, and insurtech sectors. Join Canada’s Fintech & Funding Community today FREE! Or become a contributing member and get perks. For more information, please visit: www.ncfacanada.org
The National Crowdfunding & Fintech Association (NCFA Canada) is a financial innovation ecosystem that provides education, market intelligence, industry stewardship, networking and funding opportunities and services to thousands of community members and works closely with industry, government, partners and affiliates to create a vibrant and innovative fintech and funding industry in Canada. Decentralized and distributed, NCFA is engaged with global stakeholders and helps incubate projects and investment in fintech, alternative finance, crowdfunding, peer-to-peer finance, payments, digital assets and tokens, artificial intelligence, blockchain, cryptocurrency, regtech, and insurtech sectors. Join Canada’s Fintech & Funding Community today FREE! Or become a contributing member and get perks. For more information, please visit: www.ncfacanada.org
Related Posts
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- PlatoHealth. Biotech and Clinical Trials Intelligence. Access Here.
- Source: https://ncfacanada.org/wef-forecasts-92-million-global-digital-jobs-by-2030/



