Singapore, Nigeria and Hong Kong are the three locations in the world where people are searching for the term “fintech” the most, a finding which suggests that people in these locations have the highest level of interest in the topic, a new research by the Fintech News Network (FNN) has found.
The Fintech News Network Index (FNNI), which ranks the countries and cities that are querying for the word “fintech” the most on Google, revealed that in April 2023, Internet users in Singapore, Nigeria and Hong Kong showed the most interest in the sector.
The rankings are based on search volume compared to each country’s total search volume. This means that smaller countries can have higher search interest in “fintech” compared to larger countries, even if the actual number of searches is lower.
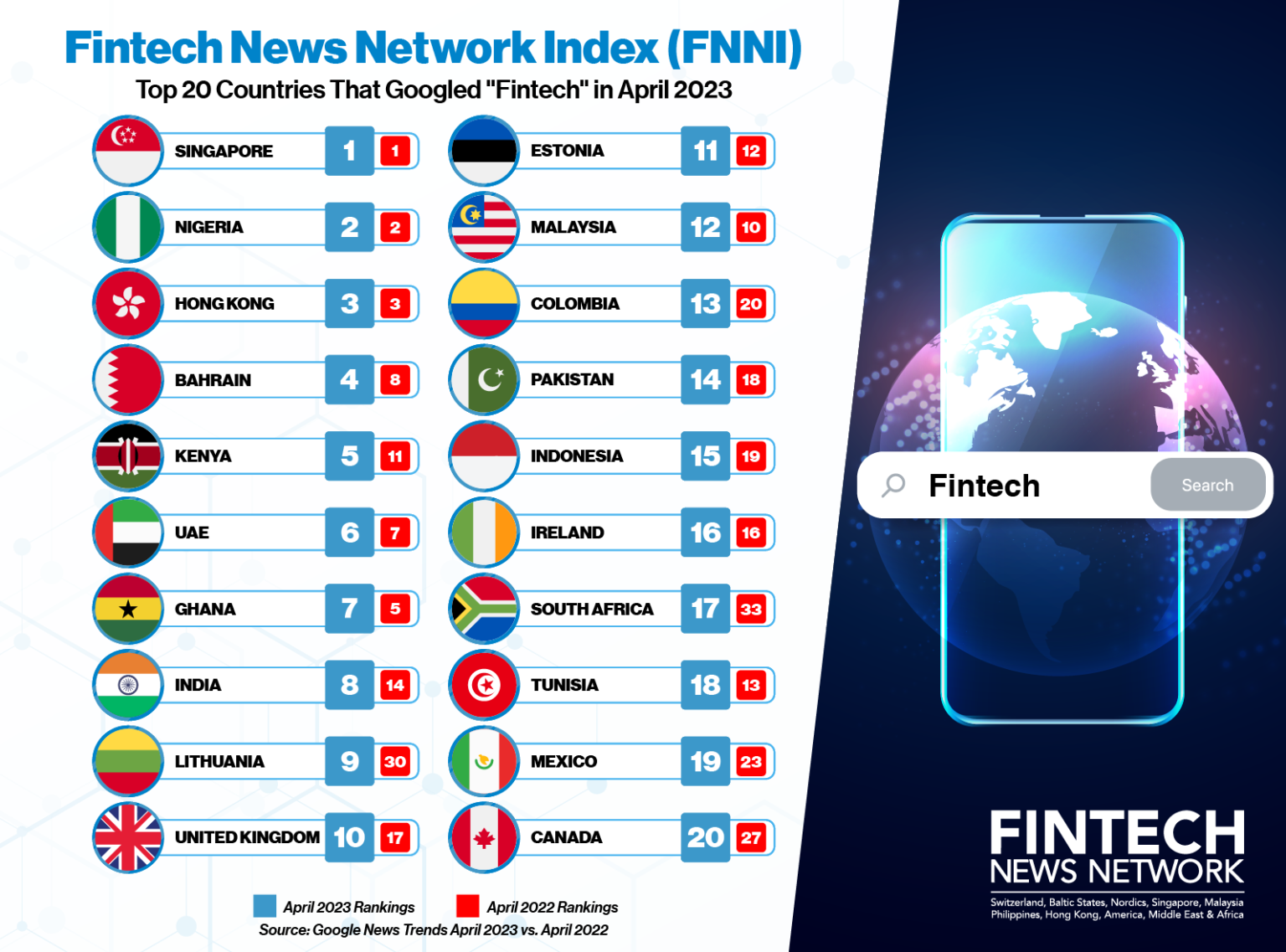
Fintech News Network Index April 2023
Singapore and Hong Kong, two prominent fintech hubs that are recognized by the global communities for their extensive ecosystems and public policies, have maintained their positions in the top three since 2021.
Southeast Asia’s fintech hub
Singapore, ranked first in both 2022 and April 2023 for “fintech” search queries, has positioned itself as a major fintech hub, acting as the gateway to the Southeast Asian region. With attractive taxation rules, advanced digitalization and supportive initiatives by the governments, Singapore attracts many companies in the fintech sector, boasting more than 1,500 ventures in the field in October 2022, a report by United Overseas Bank shows. The number means that Singapore was home to about 40% of all fintech companies in Southeast Asia’s six biggest markets last year.
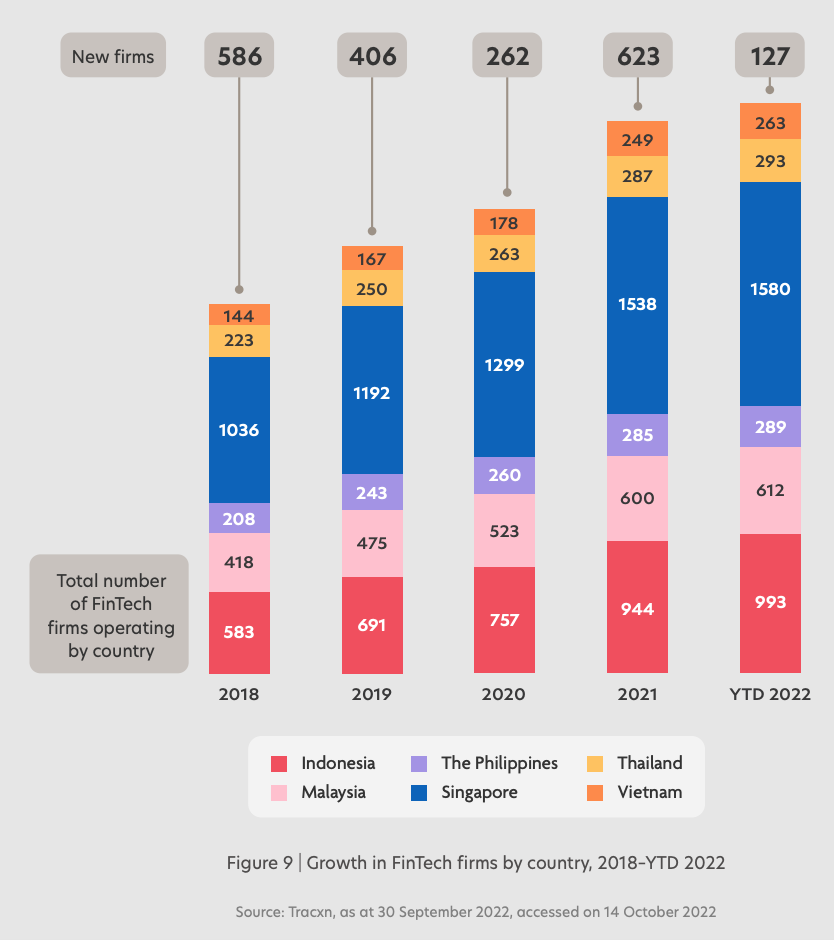
Growth in fintech firms by country, 2018 – YTD 2022, Source: Fintech in ASEAN 2022: Finance, reimagined, UOB, Singapore Fintech Association and PwC Singapore, November 2022
The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) has taken a proactive approach in developing safe and responsible cryptocurrency-related activities. The Payments Services Act (PSA), which took effect in January 2020, provides a licensing framework for various payment services, including cryptocurrency-related businesses.
So far, MAS has approved 192 Major Payment Institution licenses and 11 Digital Payment Token Service licenses. Licensed crypto service providers in Singapore include Circle, Coinhako, Paxos and Revolut.
American crypto startup Ripple is the latest company to get the green light from Singapore, announcing on June 21, 2023 that it had received in-principle regulatory approval by MAS for a Major Payments Institution license.
More rules relating to crypto are currently in the works in Singapore. In October 2022, MAS issued two consultation papers containing proposed regulatory measures relating to crypto trading and stablecoins.
The measures include not allowing businesses to lend out cryptocurrencies owned by retail customers, and to ensure customer assets are segregated from their own assets.
Stablecoin issuers, meanwhile, would be required to hold reserve assets in cash, cash equivalents or short-dated sovereign debt securities at least equivalent to 100% of the par value of the outstanding token in circulation.
In 2022, interest in fintech remained high in Singapore with fintech investments witnessing a year-on-year (YoY) rise of 22% and bucking global trends. Fintech funding hit a three-year-high of US$4.1 billion across 250 deals in mergers and acquisitions, private equity, and venture capital (VC) in 2022, according to the KPMG Pulse of Fintech H2’22.
Hong Kong pushes crypto development
Hong Kong, a prominent hub for fintech innovation in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region, ranked at second and third position in 2022 and in April 2023, respectively, in “fintech” search queries, the research show.
Hong Kong’s strategic location, well-developed financial infrastructure and supportive regulatory environment, have helped it attracted numerous fintech companies and startups. As of May 2023, the city was home to more than 800 fintech companies and over ten unicorns, according to Invest Hong Kong, the government agency responsible for foreign direct investment.
In addition, Hong Kong has one of the highest fintech adoption rates in the world. The 2023 PolyU-Asklora Fintech Adoption Index (FAI), released in April, revealed that 94% of Hong Kong consumers use at least one type of fintech products, while 74% indicated using at least two.
Rapid adoption and development of fintech in Hong Kong have been facilitated by supportive initiatives by the government, including the introduction of a virtual banking regime in 2019 that allows the establishment of virtual banks, the launch of a regulatory sandbox for fintech firms to conduct pilot trials of their innovative products and services under relaxed rules, and the launch of the Open API Framework to support open banking and data sharing.
Most recently, the city has been pushing to become a global crypto hub, rolling out on June 01, 2023 its long-awaited licensing regime for so-called virtual asset trading platforms (VATPs), pressing banks to accept crypto companies as clients and courting foreign crypto exchanges into establishing a presence in a city.
Booming interest in fintech in Nigeria
Nigeria, meanwhile, has witnessed increased interest in fintech over the past two years.
The Western African country moved up three places between 2021 and 2022, rising from the fifth to the third position. In April 2023, Nigeria rose further put, taking the second place globally.

Fintech News Network Index 2022
Booming interest in fintech in Nigeria comes at a time when the government is formally expressing its commitment to fostering the industry.
The National Fintech Strategy, released in November 2022, sets out the government’s ambition to “position Nigeria’s fintech ecosystem as a global leader”, highlighting the potential of technology and digital platforms to improve financial inclusion.
Among the major initiatives that are being undertaken, the Central Bank of Nigeria said it will design and implement balanced and proportional policies and regulations, help stimulate the domestic investment landscape, and promote multi-stakeholder collaboration.
Nigeria’s regulatory bodies are also moving forward to address demand for open banking, issuing in February 2021 a formally framework for the practice. Nigeria is among the first regulators in Africa to mandate open banking frameworks, along with financial services data protection rules.
The country already has frameworks covering peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and equity crowdfunding in place.
Nigeria’s fintech landscape has evolved tremendously, emerging over the past years into Africa’s biggest fintech hub.
The country leads the region in venture capital (VC) funding, accounting for a third of all funding deployed into fintech in the Middle East and Africa (MEA) in 2021, according to a 2022 study commissioned by Mastercard.
Nigeria is also the birth country of some of the region’s largest and most valuable fintech unicorns. These ventures include Flutterwave, a US-headquartered payment infrastructure provider originated from Nigeria and valued at US$3 billion; Opay, a mobile-based financial platform for payments, transfers, loans, savings and more valued at US$2 billion; and Interswitch, an Africa-focused integrated digital payments and commerce company worth US$1 billion and headquartered in Nigeria.
Interest in fintech remains high in the Middle East
Results from the study also revealed that interest in fintech in the Middle East remains high, with Bahrain taking the fourth position in search queries for “fintech” in April 2023, a position it has maintained since last year.
In Bahrain, the government is supporting the development of the fintech sector through various means. Regulatory bodies have launched a regulatory sandbox regime for industry stakeholders to test new products and introduced new rules covering emerging technologies and business models such as open banking, debt- and equity-based crowdfunding and digital assets.
Amendments to the so-called Crypto-Assets Module were released in March, expanding the scope of the crypto-asset activities falling under the central bank’s purview, and imposing new requirements to safeguard clients’ assets.
After Bahrain and at the fifth and sixth positions are the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Kenya, two countries that have alternated their positions since 2021. The UAE is a leading fintech hub the Middle East, home to the largest number of fintech companies in the region and most vibrant fintech ecosystem.
In 2022, the sector emerged as the preferred industry for startup investors in the UAE, accounting for 34% of total capital and 22% of transactions secured in the first half of the year.
UAE fintech companies secured a total of US$234 million in H1 2022 through 28 deals, figures which represent a threefold year-over-year (YoY) increase in total funding amount and a 65% increase in the number of rounds.
A blossoming fintech sector
Kenya, one of the fastest-growing economies in the African continent, stands out as the largest and most successful adopter of mobile wallets. The country currently ranks ahead of both the rest of the region in the use of digital payments, recording a penetration rate of 78% for digital payments, against 50% for the Sub-Saharan African region and 64% for the global average, data from a Financial Technology (FT) Partners report show.

Kenya finance and fintech products penetration, Source: FT Partners, 2023
The country has also started seeing several homegrown fintech players reach regional notoriety. M-Kopa, a startup that offers connected financing and digital financial services to underbanked consumers, recently surpassed the three million customer threshold and crossed the US$1 billion mark in total credit disbursement.
The company, which is active in Kenya, Uganda, Nigeria and Ghana, secured US$250 million in debt and equity earlier this week to further expand its financial services offering across Sub-Saharan Africa.
Buy now pay later (BNPL) startup Lipa Later was recently recognized as the third fastest-growing fintech companies in Africa by a Financial Times and Statista ranking. Across all industries, Lipa Later recorded the 16th highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in revenues between 2018 and 2021, making it one of the fastest-growing companies in the region.
This article first appeared on fintechnews.africa
Featured image credit: Edited from Freepik
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Automotive / EVs, Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- PlatoHealth. Biotech and Clinical Trials Intelligence. Access Here.
- ChartPrime. Elevate your Trading Game with ChartPrime. Access Here.
- BlockOffsets. Modernizing Environmental Offset Ownership. Access Here.
- Source: https://fintechnews.sg/72888/fintech/fintech-search-queries-most-prevalent/





