The world of cannabinoids, the active compounds found in the Cannabis sativa plant, is a complex and fascinating one. Among the many intriguing aspects of cannabinoids is the process of isomerization, a chemical reaction that transforms one isomer into another. This process has significant implications for the properties and effects of cannabinoids, and understanding it can provide valuable insights into their potential applications. In this article, we get into the intricacies of cannabinoid isomerization, drawing on the findings of peer-reviewed research to provide a comprehensive overview of this fascinating process.
What Does Isomerization Mean?
Isomerization is a process in which one molecule is transformed into another molecule with the same atoms, but with a different arrangement.
In the context of cannabinoids, isomerization can significantly alter the properties of the compound. For instance, the isomerization of cannabidiol (CBD) to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) can change a non-intoxicating compound into one that has psychoactive effects.
The Process of Cannabinoid Isomerization
The isomerization of cannabinoids is a chemical reaction that can be induced under certain conditions. According to a study by Crombie and Ponsford (1975), the isomerization of CBD to THC can be achieved by the application of heat and a catalyst such as HCl or H2SO4.
The reaction involves a shift in the position of a double bond in the CBD molecule, transforming it into THC.
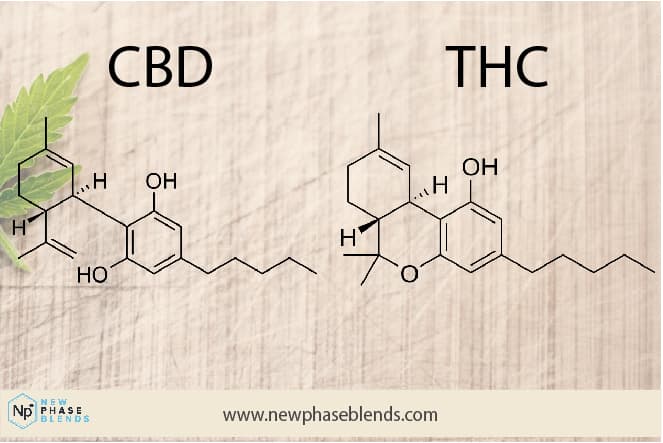

Another study found that the isomerization of CBD to THC could also be achieved using a catalyst such as p-toluenesulfonic acid in the presence of heat. This reaction also involves a shift in the position of a double bond, but the process is slightly different and results in a different isomer of THC.
Uses of Cannabinoid Isomerization
The isomerization of cannabinoids has different uses in regards to properties and potential applications. For instance, the transformation of CBD into THC through isomerization changes a non-intoxicating compound into one that has psychoactive effects.
This could potentially be used to produce THC from CBD-rich cannabis strains, although this would be subject to legal restrictions in many jurisdictions.
However, the isomerization process can also result in the formation of other cannabinoids with different properties. For instance, a study by Mechoulam and Gaoni (1967) found that the isomerization of CBD could also produce cannabichromene (CBC), another cannabinoid with potential therapeutic effects.
Where Can I See a List of Cannabinoids?
New Phase Blends maintains a comprehensive list of cannabinoids, which they differentiate between major and minor occurrences within the cannabis plant. These terms are defined by the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH). The list is constantly updated as research in the cannabis field continues to grow.


The website provides a breakdown of the known cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant, including the two primary endocannabinoids, Anandamide and 2-Arachidonoylglycerol. It also provides a search feature for users to manually look for a specific cannabinoid.
The list of major cannabinoids includes THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol), Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, and more. The minor cannabinoids, primary endocannabinoids, and isocannabinoids are also listed.
Isomerization of CBD
Isomerization of CBD, or cannabidiol, is a chemical process that transforms CBD into other cannabinoids, most notably THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). This process involves the rearrangement of the atoms within the CBD molecule to create a different molecular structure, hence a different cannabinoid.
The isomerization process typically involves the use of a catalyst, such as an acid, to facilitate the molecular rearrangement. This process has been of particular interest due to the potential to convert CBD, a non-intoxicating cannabinoid, into THC, which is psychoactive.
However, it’s important to note that this process is complex and requires precise control to ensure safety and efficacy. Furthermore, the legal implications of CBD to THC isomerization vary by jurisdiction, as THC is a controlled substance in many places.
What is Cannabinoid Conversion?
Cannabinoid conversion is a biochemical process that transforms one type of cannabinoid into another within the cannabis plant. This process is primarily driven by heat and light, which cause changes in the molecular structure of cannabinoids.
For instance, the non-psychoactive cannabinoid acid CBDA is converted into the more well-known CBD through a process called decarboxylation, which involves heating the cannabis plant. Similarly, THCA, another cannabinoid acid, is converted into the psychoactive THC through the same process.
Understanding cannabinoid conversion is crucial for both cannabis consumers and producers, as it affects the potency, effects, and therapeutic potential of cannabis products.
How is CBD Turned into Delta 8 THC?
The conversion of CBD (cannabidiol) into Delta-8-THC is a process that involves a series of chemical reactions, typically facilitated by a catalyst. This process, known as isomerization, involves the rearrangement of the atoms within the CBD molecule to form a different molecular structure, in this case, Delta-8-THC.
The process usually involves the use of an acid, such as p-toluenesulfonic acid, as a catalyst. The mixture is then heated to trigger the reaction. Read our article about CBD and Delta 8 for more information on these two cannabinoids.
Summary – Isomerization of Different Cannabinoids
The isomerization of cannabinoids is a complex process with significant implications for the properties and potential applications of these compounds. Understanding this process can provide valuable insights into the world of cannabinoids and contribute to the development of new applications and therapies. However, further research is needed to fully understand the intricacies of this process and its implications.
The process of cannabinoid isomerization, while complex, holds significant implications for the properties and potential applications of these compounds. As we continue to look into the intricacies of this process, we can hope to unlock new possibilities in the realm of cannabinoid applications and therapies. However, it’s crucial to remember that while the science is promising, further research is needed to fully understand and harness the potential of this fascinating process.
As always, any exploration of cannabinoids for therapeutic purposes should be guided by the advice of a qualified healthcare provider.
References:
- Crombie, L., & Ponsford, R. (1975). Hashish components. Photochemical production of cannabicyclol from cannabichromene. Tetrahedron Letters, 16(12), 995-998
- Repka MA, ElSohly MA, Munjal M, Ross SA. Temperature stability and bioadhesive properties of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol incorporated hydroxypropylcellulose polymer matrix systems. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2006 Jan;32(1):21-32. doi: 10.1080/03639040500387914. PMID: 16455601; PMCID: PMC2921171
-
Choudhury A, DeVine JA, Sinha S, Lau JA, Kandratsenka A, Schwarzer D, Saalfrank P, Wodtke AM. Condensed-phase isomerization through tunnelling gateways. Nature. 2022 Dec;612(7941):691-695. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05451-0. Epub 2022 Oct 20. PMID: 36265512; PMCID: PMC9771804.
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Data Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- Minting the Future w Adryenn Ashley. Access Here.
- Buy and Sell Shares in PRE-IPO Companies with PREIPO®. Access Here.
- Source: https://www.newphaseblends.com/what-is-isomerization-cannabinoids/



